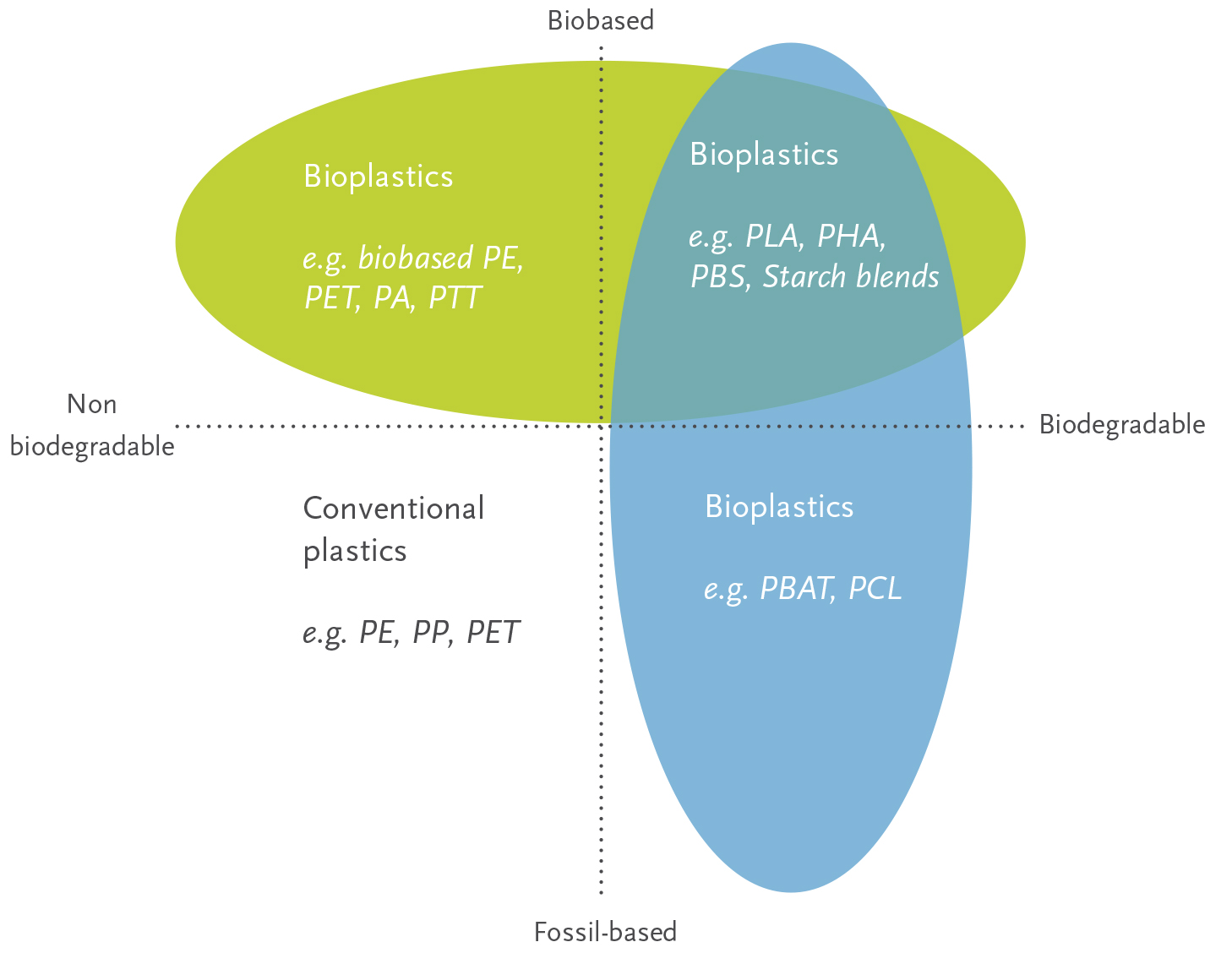
| PLA (Polylactic Acid) |
✅ (from corn/sugarcane) |
✅ (in industrial conditions) |
✅ (EN 13432) |
Packaging, 3D printing, disposables |
Industrial composting |
Brittle; poor thermal resistance |
| PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoates) |
✅ (bacterial fermentation of sugars/oils) |
✅ (home + marine) |
✅ (widely compostable) |
Medical, films, single-use items |
Biodegradable in soil, marine |
High potential but expensive |
| PBS (Polybutylene succinate) |
✅ (if bio-succinate) / ❌ (petro-based) |
✅ |
✅ (in industrial compost) |
Agricultural films, mulch, packaging |
Industrial composting |
More flexible than PLA |
| PBAT (Polybutylene adipate terephthalate) |
❌ (petroleum-based) |
✅ |
✅ (EN 13432, if blended) |
Compost bags, packaging blends |
Industrial composting |
Often blended with PLA or starch |
| PCL (Polycaprolactone) |
❌ |
✅ (very slow) |
❌ |
Specialty uses, medical, blending agent |
Biodegradable, slow in nature |
Very low melting point (~60°C) |
| bioPE (Bio-based Polyethylene) |
✅ (from sugarcane ethanol) |
❌ |
❌ |
Bottles, bags, films |
Recyclable (like fossil PE) |
Chemically identical to PE |
| PEF (Polyethylene furanoate) |
✅ (from fructose/furanics) |
❌ |
❌ |
Bottles (PET alternative) |
Recyclable |
High barrier properties; emerging tech |